|
|
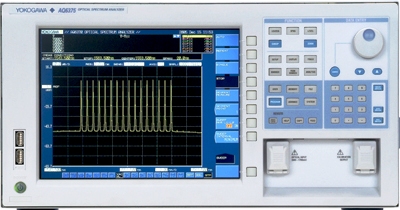
The Yokogawa AQ6375 is the first bench-top optical spectrum analyzer covering the long wavelengths over 2 µm. It is designed for researchers and engineers who have been struggling with inadequate test equipment to measure in these long wavelength ranges. The AQ6375 achieves high speed measurements with high accuracy, resolution and sensitivity, even while providing full analysis features. Troublesome calibration steps and the development of external analysis software is no longer required. The advanced monochromator achieves high wavelength resolution and high close-in dynamic range. With the sharper spectral characteristics of the monochromator, spectral signals in close proximity can be separated clearly and measured accurately. The AQ6375 can measure a pulse peak spectrum of a pulsed light signal. Often used in the transmission loop testing of telecommunication systems, and also in the low power measurement at the early stage of laser chip development to catch the peak power of a pulsed signal. Specifications. Wavelength range: 1200 to 2400 nm. Span: 0.5 nm to 1200 nm (full span), and 0 nm. Wavelength accuracy : ±0.05 nm (1520 to 1580 nm), ±0.10 nm (1580 to 1620 nm), ±0.50 nm (Full range). Wavelength repeatability: ±0.015 nm (1 min.). Wavelength resolution setting: 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1 and 2 nm. Minimum sampling resolution: 0.002 nm. Number of sampling: 101 to 50001, AUTO. Level sensitivity: -70 dBm (1800 to 2200 nm), -67 dBm (1500 to 1800 nm, 2200 to 2400 nm), -62 dBm (1300 to 1500 nm) (Sensitivity: HIGH3). Maximum input power: +20 dBm (Per channel, full wavelength range). Maximum safe input power: +25 dBm (Total input power). Level accuracy: ±1.0 dB (1550 nm, input level: -20 dBm, Sensitivity: MID, HIGH1-3). Level linearity: ±0.05 dB (Input level: -30 to +10 dBm, Sensitivity: HIGH1-3). Polarization dependence: ±0.1 dB (1550 nm). Dynamic range: 45 dB (Peak ±0.4 nm, resolution: 0.05 nm), 55 dB (Peak ±0.8 nm, resolution: 0.05 nm), (1523 nm, Sensitivity: HIGH1-3). Applicable fiber: SM, GI (50/125 µm, 62.5/125 µm). Electrical interface: GP-IB × 2 (standard/controller), RS-232, Ethernet, USB, PS/2 (keyboard), SVGA output, Analog output port, Trigger input port, Trigger output port. Display: 10.4-inch color LCD (Resolution: 800 × 600).
|